The internet is an indispensable component of modern life, keeping us connected, entertained, and informed. From Wi-Fi hotspots in coffee shops to high-speed fiber connections at home, we rely largely on the internet to meet our basic requirements. However, as technology advances, so do the ways we stay connected. A new rival, Li-Fi technology, is developing with the potential to transform how we use the internet. Could Li-Fi represent the next step forward? Let’s look at this revolutionary technology, how it works, and what obstacles it may encounter in the future.
What is Li-Fi Technology?
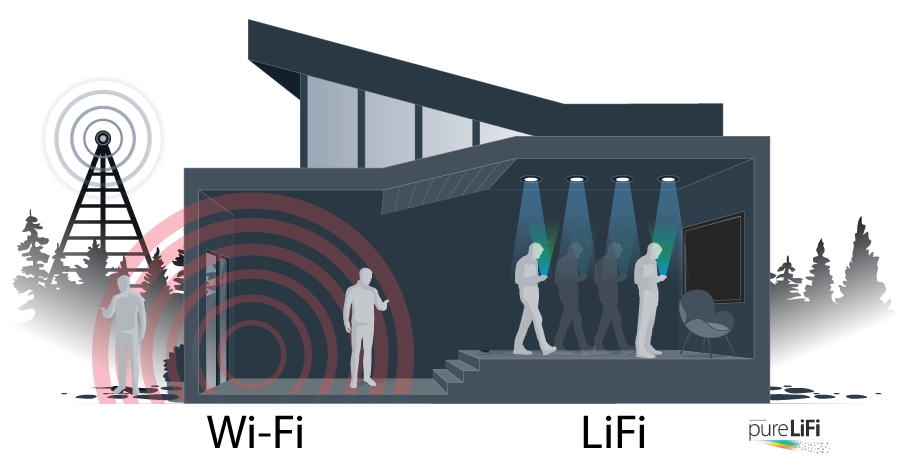
Li-Fi, or Light Fidelity, is a promising technology that uses light to communicate data. Unlike Wi-Fi, which utilizes radio waves to establish a wireless connection, Li-Fi uses visible light from LED lights to transmit data at up to 100 times the speed of Wi-Fi. This breakthrough in communication technology offers lightning-fast internet, enhanced security, and higher efficiency. But how exactly does Li-Fi function, and how does it differ from standard Wi-Fi?
How Li-Fi Works
Visible Light Communication (VLC) is the underlying technology of Li-Fi. Here’s a simple breakdown of the process:
- Data is transmitted via LED light bulbs: These bulbs blink on and off at speeds imperceptible to the human eye. The blinking pattern contains data, similar to Morse code.
- Light pulses transfer information: This information is received by appropriate devices, which can quickly decode the light signals into usable data.
- Line-of-sight requirement: Because Li-Fi employs light, communication between the source and the device must be direct.
In principle, Li-Fi can transport data at up to 224,000 megabits per second, making it a tempting option for data-intensive operations such as 4K streaming, virtual reality, and online gaming.
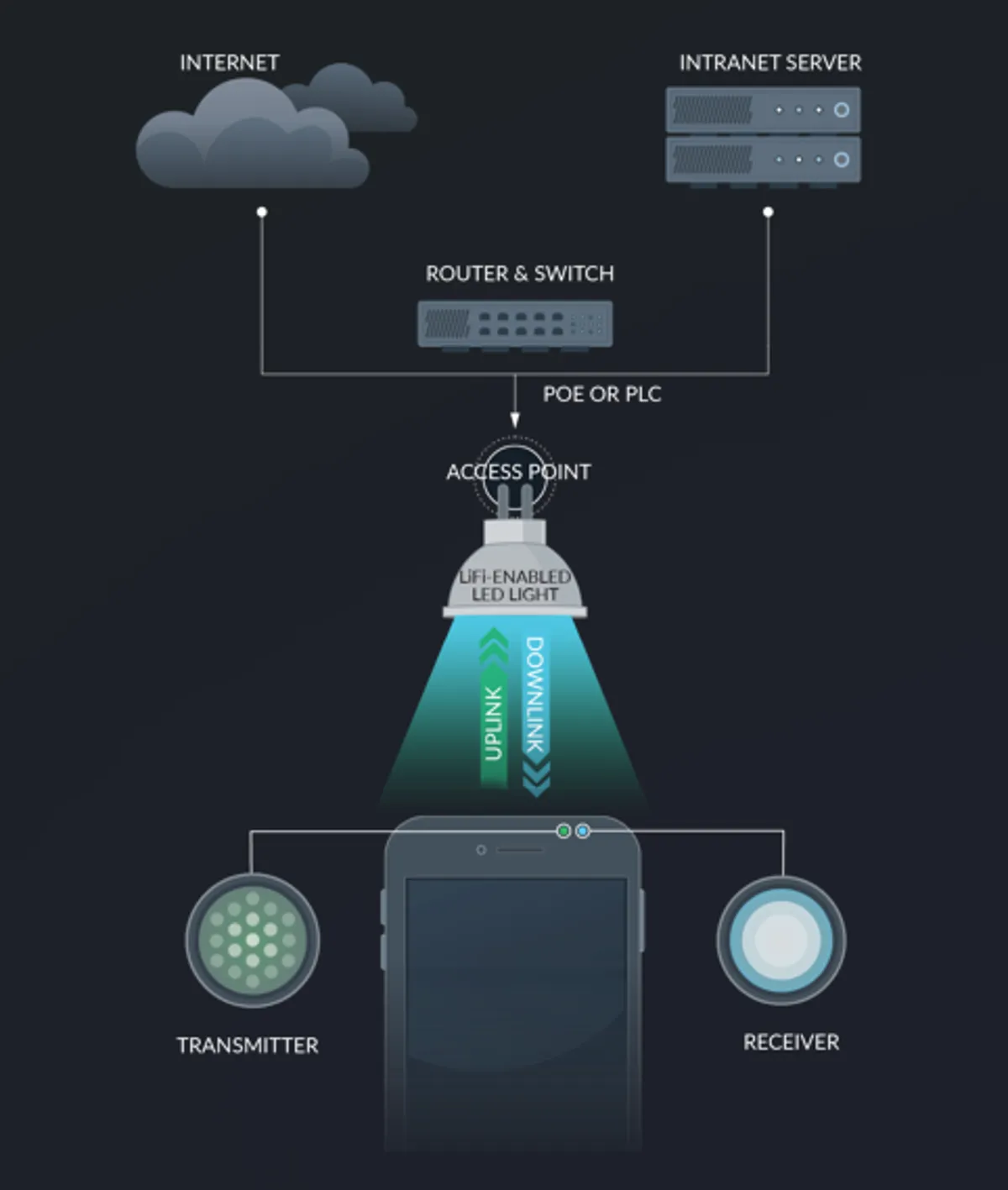
How Li-Fi Technology Could Transform the Internet
Li-Fi is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize how we connect with the internet. Here are some important areas where Li-Fi may have a large impact:
1. Speed and Efficiency
Li-Fi offers speeds much exceeding those of Wi-Fi. This could be especially advantageous in circumstances where high-speed data transport is required. For example: Consider a hospital situation in which enormous amounts of data must be sent swiftly between equipment without interruption. The high speed of Li-Fi could enable crucial systems to get real-time updates.
2. Enhanced Security
Light cannot pass through walls, so Li-Fi provides a more secure connection. Your data is limited to the illuminated area, which reduces the possibility of illegal access. For Instance, in government offices or defense industries where data security is critical, Li-Fi technology may provide a safer, more dependable means of transmitting sensitive information.
3. Less interference
Unlike Wi-Fi, which uses radio waves that are susceptible to interference from other electrical equipment, Li-Fi connections are not impacted by electromagnetic interference. For example, in locations such as airports or factories where several electronic devices are in use, Li-Fi could provide a reliable connection with no interference.
4. Energy efficiency
Li-Fi is more energy-efficient since it employs LED lights, which are already commonly utilized in homes and workplaces. Combining illumination and data transfer might dramatically reduce energy use.
The Limitations of Li-Fi Technology
While the future of Li-Fi appears bright, it is not without its downsides. Various restrictions may impede its acceptance or reduce its usefulness in certain situations.
1. Limited Range and Line-of-Sight Requirement
Li-Fi requires a direct line of sight to function, which means that the light source and the device receiving the data must be located in the same room. Walls, drapes, and even furniture might obstruct the signal. For instance, in big office areas, establishing a seamless Li-Fi network may be difficult because light sources must cover every corner to ensure continuous connectivity.
2. Compatibility issues
Many gadgets are still unable to use Li-Fi because it is a relatively new technology. Until the technology becomes more widely available, you will require specialist equipment to use it. For example, consumers may need to invest in Li-Fi-enabled cellphones, laptops, and routers, increasing the initial cost of adopting the technology.
3. No Solution for ISP-Related Speed Issues
Li-Fi cannot fix everything. If your internet service provider (ISP) provides sluggish connections or throttles your connection, Li-Fi will not suddenly improve the speed. Your provider continues to determine your overall internet speed.
Pros and Cons
- Faster data transmission than Wi-Fi
- Enhanced security due to confined light signals
- No electromagnetic interference
- Energy efficient with LED use
- Requires direct line of sight
- Limited range due to light barriers
- Compatibility with devices is still limited
- Doesn’t address ISP speed issues
Potential Use Cases for Li-Fi Technology
Li-Fi has the potential to disrupt multiple sectors and improve connection in specialized settings. Here are some examples of how Li-Fi technology could make a difference:
1. Smart Cities
Li-Fi’s high-speed, low-latency characteristics could help to construct smart cities, in which real-time data powers everything from traffic control to public safety.
2. Virtual reality
Li-Fi’s reduced latency could improve virtual and augmented reality experiences by enabling seamless connectivity for immersive gaming and training applications.
3. Healthcare
In medical settings where radio wave interference could be deadly, Li-Fi could enable quick, interference-free communication between devices, thereby enhancing patient care.
FAQs
1. How does LiFi vary from Wi-Fi?
Li-Fi uses visible light to transport data, whereas Wi-Fi uses radio waves. Although Li-Fi has the potential to be faster and more secure, its range is limited due to its reliance on direct light transmissions.
2. Is Li-Fi accessible for consumer use?
Li-Fi is still in the experimental phase, but it is predicted to be commercially available between 2024 and 2029. Some businesses, such as defense and healthcare, have already begun testing it.
3. Will Li-Fi replace Wi-Fi?
Li-Fi is unlikely to completely replace Wi-Fi, but it will complement it. In situations where security, speed, and interference-free connections are required, Li-Fi may be the preferred alternative.

Conclusion
Li-Fi technology shows enormous potential as a speedier and more secure alternative to Wi-Fi. Although it is still in its early phases, Li-Fi has the potential to alter how we connect to the internet in areas such as healthcare, government, and smart cities. However, because it is based on light signals and requires suitable devices, its initial influence may be limited. As research progresses and more firms invest in the development of Li-Fi, we may see this technology become an essential component of our internet infrastructure. As Li-Fi approaches commercial practicality in the next years, it will be fascinating to witness how technology alters our perceptions of internet connectivity.
